Recognition of Plausible Therapeutic Agents to Combat COVID-19: An Omics Data Based Combined Approach
Abstract
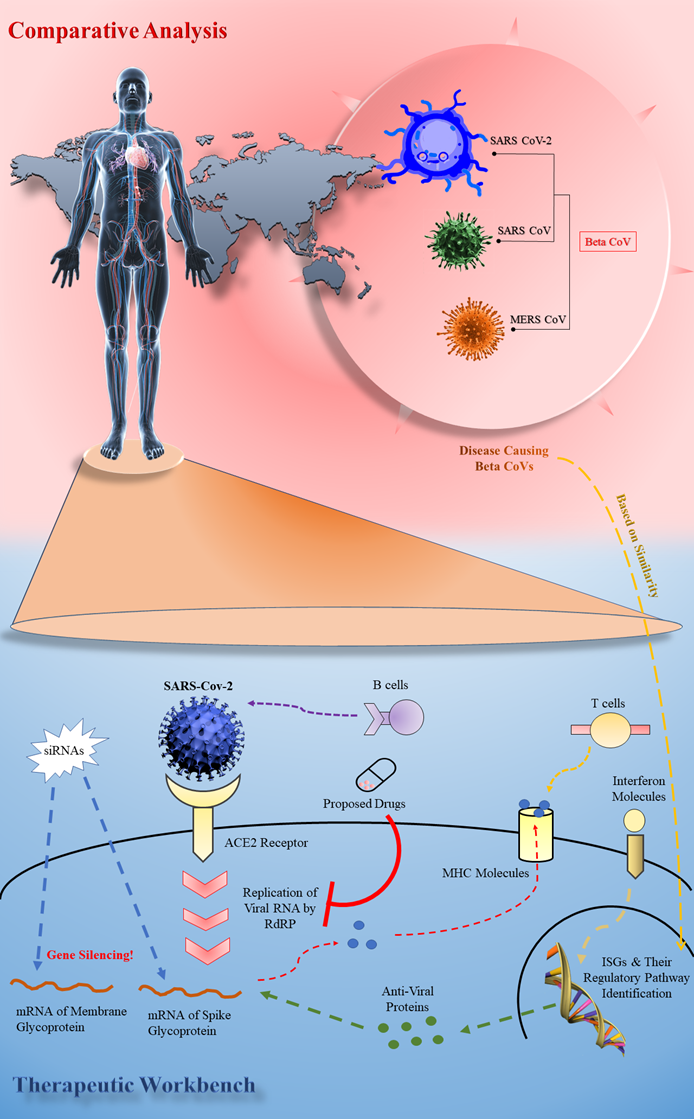
Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) has become an immense threat to global public health. The causative agent of this disease is a novel zoonotic pathogen called Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome related Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). Since this is a newly evolved pathogen, very limited information is available to develop effective therapeutics against this deadly virus. Although bioinformatics based analysis could be handy to unveil drugs or vaccines against bacteria and fungus, such approaches are hardly seen for acellular viruses. However, in this study we rationally merged several powerful in silico techniques and proposed prospective therapeutics based on available omics data for COVID-19. Through meticulous analysis of conserved regions of 67 SARS-CoV-2 strains, spike and membrane glycoproteins were chosen to develop and propose a chimeric vaccine against this virus. siRNAs were also designed against these glycoprotein genes to silence them. Moreover, six drug compound candidates were suggested to inhibit the conserved RNA-directed RNA polymerase protein. Finally, due to the close relationship of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV, publicly available gene expression datasets of SARS-CoV were analyzed to identify 13 immunoregulatory genes that might develop interferon based therapy. Our study will quicken the researches among pharmaceuticals, researchers and clinicians to develop rapid therapeutics for controlling this notorious pandemic disease.